Why a Dish Needs to Hit 160 Degrees to Really be Clean
In the restaurant industry, sanitation is a key concern for a successful business. Health code requires certain minimal standards, but more importantly is a basic ethical approach to food service involving not making customers become sick. Obviously regular hand washing is a key part of the concept, but as important is proper dishwashing in which in which storage containers, cookware, and serving dishes reach a minimum temperature of 160° to assure thorough sanitation.
Typical Food Borne Bacteria
There are common bacteria which cause sickness in the form of bacterial food poisoning. Often called a “stomach bug,” when someone becomes sick they aren't typically aware of which one they have if they don't see a doctor and have it formally diagnosed.
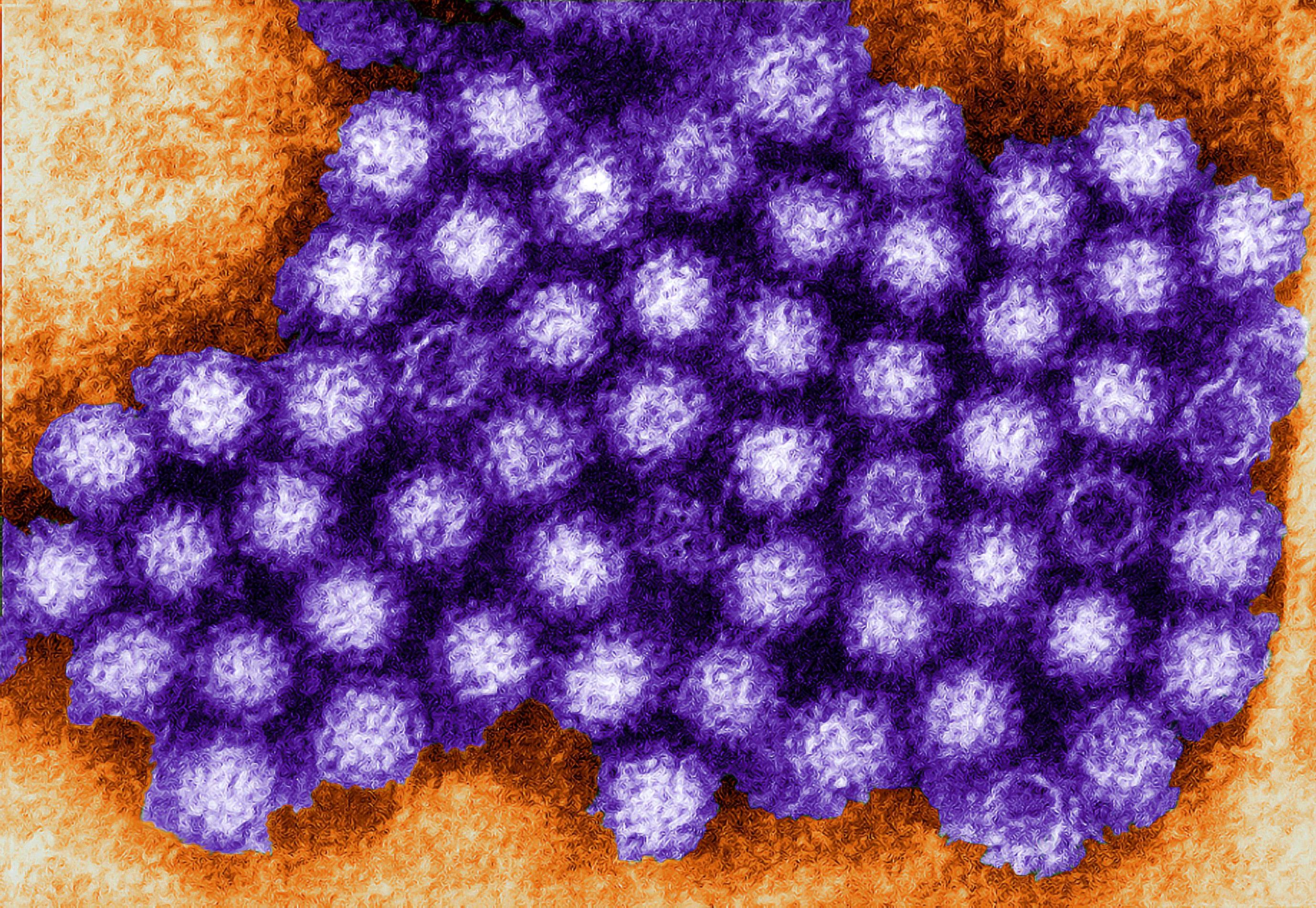
- Norovirus is a common bacteria which is easy to contract and quite contagious. If your family has ever been sick in turn and it seems you keep giving the sickness back and forth to each other, Norovirus was likely the culprit.
- Salmonella is perhaps the best known of bacterial infections and is present on many raw foods. Although cooking removes the bacteria assuming the inner portion of the food reaches a temperature of 150°, any utensils or surfaces used to prep the food remains infected.
- Listeria can be a particularly dangerous bacteria as it is able to grow even in refrigeration. Poisoning via Listeria typically resembles a mild flu condition, but can be lethal for small children or the elderly.
- Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is the typical bacterial variant in foods which are prepared after cooking, such as salads, especially the mayonnaise varieties such as potato or chicken salad. Preventing an outbreak requires diligent hand washing before and after handling each component of the recipe along with proper refrigeration of the food and of course, cleaning the dishes used during storage and serving.
- Clostridium botulinim, commonly known as botulism, is one of the rarer bacteria but is is more likely to be a fatal infection rather than causing simple stomach problems for a few days. It's important to properly sanitize everything used for canning foods, and boil the food well before serving after the seal is broken.
Proper Cleaning Temperatures
Because most bacteria are killed at a temperatures between 140°-150°, 160° is considered a safe industry standard to assure a dish or utensil has been properly sanitized. To assure the dishwasher is properly achieving this goal, use of irreversible thermometer strips known as Thermolabel® is recommended. The strip is easy to use and read as it unmistakably turns black upon reaching a safe temperature, meaning any contagion on the dishes being washed has been killed. Contact Paper Thermometer Temperature-Indicating Devices for details about what products are offered and which would be best for your situation and the equipment your kitchen uses.
Sources: http://aggie-horticulture.tamu.edu/food-technology/bacterial-food-poisoning/
